-
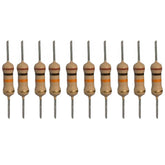
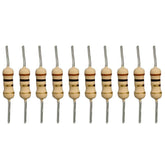
10k Ohm Resistor - Pack of 1010k Ohm Resistor - Pack of 10 Resistors are electronic components that have a specific, never-changing electrical resistance. The resistor's resistance limits the flow of electrons through a circuit. They are passive components, meaning they only consume power (and can't generate it). Resistors are usually added to circuits where...
- Rs. 10
Rs. 14- Rs. 10
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 4 -
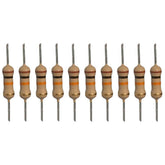
330 Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)330 Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 330 ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that...
- Rs. 9
Rs. 15- Rs. 9
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 6 -
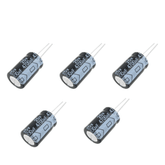
100uF / 25V Electrolytic Capacitor (Pack of 5)100uF / 25V Electrolytic Capacitor High quality 100uF/25V radial electrolytic capacitors. Work great as voltage noise suppressors for voltage regulators and for power supply. Putting one of these across power and ground in each of your projects ensures a smooth noise resistant power supply...
- Rs. 22
Rs. 39- Rs. 22
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 17 -
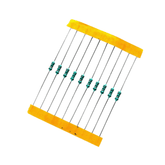
100 Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)100 Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 100 ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements...
- Rs. 11
Rs. 15- Rs. 11
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 4 -
1N4148 Diode - (Pack of 10)1N4148 Diode - (Pack of 10) The speciality of this 1N4148 Diode is its fast recovery time of 8ns at a forward current of 10mA, hence this diode is used in places where fast switching is involved. 1N4148 is a standard diode made up of silicon and is used for extremely...
- Rs. 29
Rs. 39- Rs. 29
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 10 -
0.1 uF 50V Ceramic Capacitor (Pack of 10)0.1 uF 50V Ceramic Capacitor (Pack of 10) Ceramic capacitors are great for filtering out noise above 1KHz. Power spikes and other noise can cause all sorts of weird things to happen in your project so having a few of these should help quite...
- Rs. 14
Rs. 19- Rs. 14
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 5 -
2.2k Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)2.2k Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 2.2k ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements...
- Rs. 11
Rs. 15- Rs. 11
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 4 -
470 Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)470 Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 470 ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements...
- Rs. 9
Rs. 15- Rs. 9
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 6 -
1N5408 Diode - (Pack of 10)1N5408 Diode - (Pack of 10) The 1N5408 diode is called a power diode because of its high forward current and reverse voltage with a power dissipation of 6.25W. For 1N5408 Diode, the maximum current carrying capacity is 3A it withstands peaks up to 200A. Hence we can...
- Rs. 33
Rs. 45- Rs. 33
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 12 -
1M Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)1M Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 1M ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements...
- Rs. 9
Rs. 15- Rs. 9
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 6 -
4700uF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor (Pack of 5)4700uF 25V Electrolytic Capacitor A 4700uF (microfarad) 25V electrolytic capacitor is a type of passive electronic component that stores electrical charge and is commonly used in electronic circuits for filtering, decoupling, and energy storage. It is called an electrolytic capacitor because it uses an...
- Rs. 99
Rs. 149- Rs. 99
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 50 -
47k Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)47k Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) 47k ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. Also check pack of 10 220k-ohm resistors available on the...
- Rs. 11
Rs. 13- Rs. 11
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 2 -
220k Resistor (Pack of 10)220k Resistor (Pack of 10) The carbon film resistor is a 22k ohm resistor with 5% tolerance. It is a type of fixed resistor that uses carbon film to restrict the electric current to certain level. These types of resistors are widely used in...
- Rs. 32
Rs. 35- Rs. 32
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 3 -
1 Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)1 Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 1 ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements...
- Rs. 10
Rs. 15- Rs. 10
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 5 -
33k Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)33k Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 33k ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements...
- Rs. 11
Rs. 15- Rs. 11
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 4 -
3.3k Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)3.3k Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 3.3k ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements...
- Rs. 11
Rs. 15- Rs. 11
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 4 -
10M Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10)10M Ohm Resistor - (Pack of 10) The 10M ohm Carbon Film Resistors are typical axial-lead resistors, which have much better temperature stability and provide lower noise, and are generally better for high frequency or radiofrequency applications. A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements...
- Rs. 11
Rs. 15- Rs. 11
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 4 -
TIP31C NPN Power Transistor - (Pack of 5)TIP31C NPN Power Transistor - (Pack of 5) TIP31C is a three-layer NPN device within the working range, the collector current IC is a function of the base current IB, a change in the base current giving a corresponding amplified change in the collector...
- Rs. 48
Rs. 69- Rs. 48
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 21 -
100KPF Ceramic Cap (Pack of 20)100KPF Ceramic Cap A 100KPF ceramic capacitor is a type of capacitor that is made of ceramic material and has a capacitance value of 100,000 picofarads (pF). A capacitor is an electronic component that stores an electrical charge and is commonly used in circuits...
- Rs. 21
Rs. 24- Rs. 21
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 3 -
16MHz Crystal Oscillator - (Pack of 10)16MHz Crystal Oscillator - (Pack of 5) The 16 MHz crystal oscillator circuit sustains oscillation by taking a voltage signal from the quartz resonator, amplifying it, and feeding it back to the resonator. It provides clock pulses of 8 MHz frequency. The popularity of the...
- Rs. 72
Rs. 107- Rs. 72
- Unit price
- per
Save Rs. 35

Best Price Guarantee

Ready Stock for Bulk Purchase
Dedicated Account Managers

5% GST Benefits for Eligible SEZ and Edu
Technical Support Available

1-Year Manufacturer Warranty