Drone Part List
Summary
In the world of technology, drones have become increasingly popular. But do you want to know what exactly is a drone, and what materials are used to make one? If the answer is yes! then check this blog post which explores these questions and provides a list of the 10 essential drone parts needed to build your own drone. Whether you're a hobbyist or interested in the technical aspects of drone technology, this post is sure to provide valuable insights.
Introduction
Explore the world of drones with our ultimate guide to drone parts! Discover everything you need to know about these amazing flying machines, from the frame to the electronic controllers. Whether you're new to drones or a seasoned enthusiast, we've got you covered.
Learn about the key components like flight controllers, propellers, and motors. Get ready for an exciting journey into drone technology!
What is a Drone?
The term “drone” usually refers to any unpiloted aircraft. These craft, also known as "Unmanned Aerial Vehicles" (UAVs), are capable of a wide range of tasks, from military operations to package delivery.
Drones are available in a variety of sizes, ranging from the size of a plane to the size of your hand. We covered compete drone part list in this blog.

An unmanned aircraft is referred to as a drone. Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or unmanned aircraft systems are other terms for drones. A drone is a flying robot that can be controlled remotely or fly autonomously using software-controlled flight plans in its embedded systems, which work in conjunction with onboard sensors and a global positioning system (GPS).
UAVs were most often associated with the military. Initially, they were used as anti-aircraft target practice, intelligence gathering, and, more controversially, as weapons platforms. Drones are now used in a variety of civilian applications, including:
- Search and Rescue
- Surveillance
- Traffic Monitoring
- Weather monitoring
- Firefighting
- Personal use
- Drone-based photography
- Videography
- Agriculture
- Delivery services
read more : Working of A Drone
What are the materials or components is used to make a drone?
All drone parts and components are vital to a smooth and safe flight. Knowing how a drone works will give you more confidence when flying. You'll also know which components to inspect regularly, as well as which diy drone parts are simple to replace or upgrade.
If you're having trouble flying your drone, knowing what each parts of drone does will help you a lot in figuring out what's wrong.
read more : Drone Motor – Where to Begin?
10 Drone Parts Everybody Required to Build Drone
1. Quadcopter Frame

This is a structure (frame) in which all the other parts of drone fit. It functions as a skeleton, with various components arranged in such a way that the drone's center of gravity is evenly distributed.
Different drone frame structures are used for different drone designs, with a minimum of three propeller fitting gaps. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
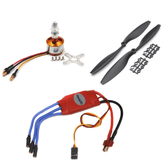
2. Motors

Motors are essential for the propeller’s rotation. This enhances the thrust force for propelling the drone. The number of motors should, however, be equal to the number of propellers.
The drone motors are also mounted in such a way that the controller can easily rotate them. Their rotation improves the direction control of the drone. For the drone's efficiency, selecting the right motor is critical.
Various parameters, such as voltage and current, thrust and thrust-to-weight ratio, power, efficiency, and speed, must all be carefully examined.
read more : Drone motor maintenance
3. Electronic Speed Controllers (ESC)
This is an electronic control board that varies the motor’s speed. It also acts as a dynamic brake. The component supports the ground pilot in estimating the drone's height while in flight.
This is achieved by calculating the total amount of power consumed by all of the motors. The loss of power from the power reservoirs is linked to altitude.
read more : How to choose ESC for Quadcopter
4. Flight Controller Boards

The drone's takeoff location is recorded on the flight board in case the drone must return to its takeoff location without being guided. This is known as the ‘return to home’ feature. It also determines and calculates the drone’s altitude for the amount of power it consumes.
read more : Best flight controller for drone
Most commonly used fight controller boards
- Openpilot CC3D Flight Controller
- APM 2.8 Flight controller board
- KK 2.1.5 Multi-Rotor LCD Flight Control Board
5. Propellers

Propellers are clove-like blades structured to create a difference in air pressure. These drone parts cut through the air when in motion, creating a pressure difference between the top and bottom of the rotors. Low pressure on the top side compared to the bottom side causes the drone to lift into the air.
Learn how to select the best drone propeller for better lift.
Drone propeller explained: What you need to know.
6. Radio Transmitter

It is a channeled transmitter and a communicator to the drone. Each channel has a specific frequency capable of steering the drone in a certain motion. Drones require at least 4 channels for effective operation.
read more : Drone transmitter and receiver guide
7. Battery, Electronics, and Power Distribution Cables

LiPo batteries are among the most common battery types used for drones because they offer the advantage of high energy density to their size and weight, with a higher voltage per cell, so they can power the drone's onboard systems with fewer cells than other rechargeable.
The electrical and electronic drone parts are crucial part pertaining to the control and operation of the drone. However, with respect to the purpose of the drone, other components can be either included or omitted. The drone may be functional without these parts, though for multitasking purposes it’s advised to include them.
read more : Affordable drone batteries
8. Camera
The drones have cameras attached to them for video footage. Cameras with video recording, storage, and transmission capabilities are available and used according to the operator's preferences or budget. Some people use their own cameras, while others prefer GoPro cameras.
9. Landing Gear

This is a structure for landing the drone safely. It can, however, be exempted because an experienced user can balance the motor's speed for a safe landing in an emergency. There are two major types of the landing gear. One is fixed landing gear and the other is the retractable landing gear.
10. First-Person Video
It is more expensive than a standard control device interface (transmitter) screen, but it provides the user with an interactive 3D view experience. The first-person view (FPV) provides the user with the sensation of flying.
An FPV system is made up of two main parts. The ground component is the first. The ground component is also called the ground station. On the ground, it consists of a video receiver and a display system.
The video receiver is the second major component. The data is received by the video receiver by matching its frequency to that of the drone's transmitter. 433 MHz, 869 MHz, 900 MHz, 1.2 GHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5.8 GHz are the most commonly used frequencies for video transmission.
The antennas on advanced versions of ground components are more sophisticated, resulting in higher image resolution.
The drone's airborne component includes a camera and a video transmitter. A basic FPV system consists of the following components. Advanced FPV systems, on the other hand, have advanced components and functions.
It's important to select the right parts of drone for your drone based on your needs. You are the one who will be flying the drone, so you are the expert. The components are widely available in a variety of stores

Create your own drone from scratch with this Drone Kit.
Conclusion
The above guide shows the parts of drone required for building a Drone and how to choose them as per the requirements. Choosing the diy drone parts varies as per the requirements.
If you appreciate our work don't forget to share this post and leave your opinion in the comment box.
Please do check out other blog posts about Popular electronics
Check out other related blog posts about Drones: Drone transmitter and receiver , Drone motors and Getting started with a Quadcopter
Make sure you check out our wide range of products and collections (we offer some exciting deals!)
Excerpt
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which Motors are used in drones?
In general, there are two types of motors used in drones.
2. Which battery is used in drones?
a. Brushed motors: (aka DC, coreless)
3. How to buy drone parts?
This motor can be found in every toy-grade multirotor, including the Syma X5, Blade Nano QX, UDI 818A, and others. Coreless motors are used in the Parrot AR Drone as well. Smaller coreless motors resemble tall, gleaming silver spray paint cans. If your multirotor is bigger than your palm, and it uses gears to transfer motor power to the propellers, it's probably got coreless motors.Pros: Coreless motors are cheap to manufacture, simple to wire, compact, and lightweight.Cons: Coreless motors have a short lifespan, depending on their size. (The larger the motor, the longer it usually lasts.) The ones used in toy drones generally have between 0 - 6 hours of total run-time before they burn out. Brushless motors, on the other hand, are more powerful than coreless motors. (However, this makes coreless motors safer around children, pets, walls, and other objects.)Some of the drones which come with the brushed (coreless motors):DIY Drone Kit with WiFi and CameraDIY Drone Kit With Manual (Camera Not Included)
4. Where can I buy drone parts?
b. Outrunner Brushless:These are the motors that are commonly found on photography multirotor, such as high-powered drones. Brushless motors vary in appearance depending on the manufacturer, but they are typically short and stout. Brushless multirotor almost always have their propellers mounted directly to the motor shafts.Pros: Brushless motors are extremely powerful, provide excellent torque without the use of gears, and have a long lifespan if properly maintained. Brushless motors can run for much longer periods of time without experiencing heat damage than their coreless counterparts (the heat may temporarily reduce the performance of brushless motors, to a degree, but once they cool down, their performance should revert to normal.)Cons: Brushless motors are more expensive than coreless motors, and they require electronic components such as ESCs (Electronic Speed Controllers) to operate. Brushless motors are more dangerous to nearby objects due to their increased power (like fingers).
5. Where to buy drone parts near me?
Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries are among the most popular battery types for drones because they have a high energy density compared to their size and weight, as well as a higher voltage per cell, allowing them to power the drone's onboard systems with fewer cells than other rechargeable. The LiPo batteries are available in many variants and types. The main things to keep in mind while choosing the right battery for the drone are to look into the voltage and current rating, discharge current, charging voltage and current ratings, and also the ampere-hour rating which shows the amount of power that the battery can store.
6. What are the essential parts required to build a drone?
To build a drone, you'll need several essential parts: a flight controller, motors, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), a drone frame, propellers, a battery, a transmitter, and a receiver. Optional components like GPS modules and cameras enhance functionality. Each piece plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth flight and maneuverability.
7. What does a drone flight controller do?
A drone flight controller is the brain of the drone, responsible for processing commands and stabilizing flight. It collects data from sensors and adjusts motor speeds for optimal control and handling. This component is vital for functions like autonomous flying, GPS navigation, and flight stabilization, ensuring a safe and responsive flight experience.
8. How do motors and ESCs work together in a drone?
In a drone, motors and electronic speed controllers (ESCs) work in tandem to regulate speed and power. The ESC receives signals from the flight controller and adjusts the voltage to the motors. This collaboration allows precise control over the drone's movements, impacting acceleration, deceleration, and stabilization during flight.
9. What type of battery is best for drones?
Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are the best choice for drones due to their high energy density and lightweight properties. They provide excellent performance and quick discharge rates, essential for drone agility. Consider the battery's voltage and capacity to match your drone's requirements for optimal flight time and power delivery.
10. How do propellers affect drone flight and stability?
Propellers significantly influence a drone's flight and stability. Their size and pitch affect lift and thrust, impacting speed and agility. Well-matched propellers ensure stable flight, while oversized or poorly pitched ones can lead to inefficiency or instability. Choosing the right propeller is crucial for achieving balanced performance and controlled maneuvers.
11. What is the role of GPS in a drone setup?
GPS in a drone setup enhances navigation and positioning accuracy. It allows the drone to determine its location, enabling features like waypoints, return-to-home functionality, and altitude hold. With GPS, drones can execute automated flight paths and maintain stability, making them ideal for aerial photography and surveying tasks.
12. How can I choose the right drone frame for my build?
Choosing the right drone frame involves considering size, material, and design. A lightweight frame enhances agility, while a sturdier frame offers durability. Ensure the frame design accommodates all your components, including motors and battery. Compatibility with your planned drone type—racing, photography, or freestyle—is also crucial in your selection.
13. What kind of transmitter and receiver should I use?
Select a transmitter and receiver based on your needs and skill level. For beginners, a basic 2.4GHz system is suitable, offering a reliable range. Advanced users may prefer systems with telemetry features, allowing real-time data feedback. Ensure compatibility with your flight controller and choose a transmitter with sufficient channels for your specific drone setup.
14. What are FPV cameras used for in drones?
FPV (First Person View) cameras allow pilots to experience real-time video feeds directly from the drone. Used mainly in racing and aerial photography, these cameras enhance control and situational awareness. They enable immersive flying experiences, making it easier to navigate obstacles and capture stunning footage from unique perspectives.
15. How do I assemble and test my drone safely?
To assemble and test your drone safely, start by following a detailed guide for each component. Ensure all connections are secure and double-check wiring. Once assembled, conduct a pre-flight check to confirm battery levels and control inputs. Test in an open area, away from people and obstacles, to minimize risks during flight trials.
1. Which Motors are used in drones?
In general, there are two types of motors used in drones.
2. Which battery is used in drones?
a. Brushed motors: (aka DC, coreless)
3. How to buy drone parts?
This motor can be found in every toy-grade multirotor, including the Syma X5, Blade Nano QX, UDI 818A, and others. Coreless motors are used in the Parrot AR Drone as well. Smaller coreless motors resemble tall, gleaming silver spray paint cans. If your multirotor is bigger than your palm, and it uses gears to transfer motor power to the propellers, it's probably got coreless motors.Pros: Coreless motors are cheap to manufacture, simple to wire, compact, and lightweight.Cons: Coreless motors have a short lifespan, depending on their size. (The larger the motor, the longer it usually lasts.) The ones used in toy drones generally have between 0 - 6 hours of total run-time before they burn out. Brushless motors, on the other hand, are more powerful than coreless motors. (However, this makes coreless motors safer around children, pets, walls, and other objects.)Some of the drones which come with the brushed (coreless motors):DIY Drone Kit with WiFi and CameraDIY Drone Kit With Manual (Camera Not Included)
4. Where can I buy drone parts?
b. Outrunner Brushless:These are the motors that are commonly found on photography multirotor, such as high-powered drones. Brushless motors vary in appearance depending on the manufacturer, but they are typically short and stout. Brushless multirotor almost always have their propellers mounted directly to the motor shafts.Pros: Brushless motors are extremely powerful, provide excellent torque without the use of gears, and have a long lifespan if properly maintained. Brushless motors can run for much longer periods of time without experiencing heat damage than their coreless counterparts (the heat may temporarily reduce the performance of brushless motors, to a degree, but once they cool down, their performance should revert to normal.)Cons: Brushless motors are more expensive than coreless motors, and they require electronic components such as ESCs (Electronic Speed Controllers) to operate. Brushless motors are more dangerous to nearby objects due to their increased power (like fingers).
5. Where to buy drone parts near me?
Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries are among the most popular battery types for drones because they have a high energy density compared to their size and weight, as well as a higher voltage per cell, allowing them to power the drone's onboard systems with fewer cells than other rechargeable. The LiPo batteries are available in many variants and types. The main things to keep in mind while choosing the right battery for the drone are to look into the voltage and current rating, discharge current, charging voltage and current ratings, and also the ampere-hour rating which shows the amount of power that the battery can store.
6. What are the essential parts required to build a drone?
To build a drone, you'll need several essential parts: a flight controller, motors, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), a drone frame, propellers, a battery, a transmitter, and a receiver. Optional components like GPS modules and cameras enhance functionality. Each piece plays a crucial role in ensuring smooth flight and maneuverability.
7. What does a drone flight controller do?
A drone flight controller is the brain of the drone, responsible for processing commands and stabilizing flight. It collects data from sensors and adjusts motor speeds for optimal control and handling. This component is vital for functions like autonomous flying, GPS navigation, and flight stabilization, ensuring a safe and responsive flight experience.
8. How do motors and ESCs work together in a drone?
In a drone, motors and electronic speed controllers (ESCs) work in tandem to regulate speed and power. The ESC receives signals from the flight controller and adjusts the voltage to the motors. This collaboration allows precise control over the drone's movements, impacting acceleration, deceleration, and stabilization during flight.
9. What type of battery is best for drones?
Lithium Polymer (LiPo) batteries are the best choice for drones due to their high energy density and lightweight properties. They provide excellent performance and quick discharge rates, essential for drone agility. Consider the battery's voltage and capacity to match your drone's requirements for optimal flight time and power delivery.
10. How do propellers affect drone flight and stability?
Propellers significantly influence a drone's flight and stability. Their size and pitch affect lift and thrust, impacting speed and agility. Well-matched propellers ensure stable flight, while oversized or poorly pitched ones can lead to inefficiency or instability. Choosing the right propeller is crucial for achieving balanced performance and controlled maneuvers.
11. What is the role of GPS in a drone setup?
GPS in a drone setup enhances navigation and positioning accuracy. It allows the drone to determine its location, enabling features like waypoints, return-to-home functionality, and altitude hold. With GPS, drones can execute automated flight paths and maintain stability, making them ideal for aerial photography and surveying tasks.
12. How can I choose the right drone frame for my build?
Choosing the right drone frame involves considering size, material, and design. A lightweight frame enhances agility, while a sturdier frame offers durability. Ensure the frame design accommodates all your components, including motors and battery. Compatibility with your planned drone type—racing, photography, or freestyle—is also crucial in your selection.
13. What kind of transmitter and receiver should I use?
Select a transmitter and receiver based on your needs and skill level. For beginners, a basic 2.4GHz system is suitable, offering a reliable range. Advanced users may prefer systems with telemetry features, allowing real-time data feedback. Ensure compatibility with your flight controller and choose a transmitter with sufficient channels for your specific drone setup.
14. What are FPV cameras used for in drones?
FPV (First Person View) cameras allow pilots to experience real-time video feeds directly from the drone. Used mainly in racing and aerial photography, these cameras enhance control and situational awareness. They enable immersive flying experiences, making it easier to navigate obstacles and capture stunning footage from unique perspectives.
15. How do I assemble and test my drone safely?
To assemble and test your drone safely, start by following a detailed guide for each component. Ensure all connections are secure and double-check wiring. Once assembled, conduct a pre-flight check to confirm battery levels and control inputs. Test in an open area, away from people and obstacles, to minimize risks during flight trials.


















2 Comments
Thanks for the giving me the Knowleg about the drown
Remote