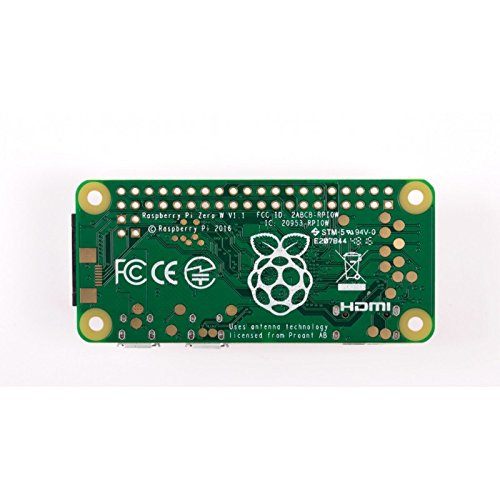
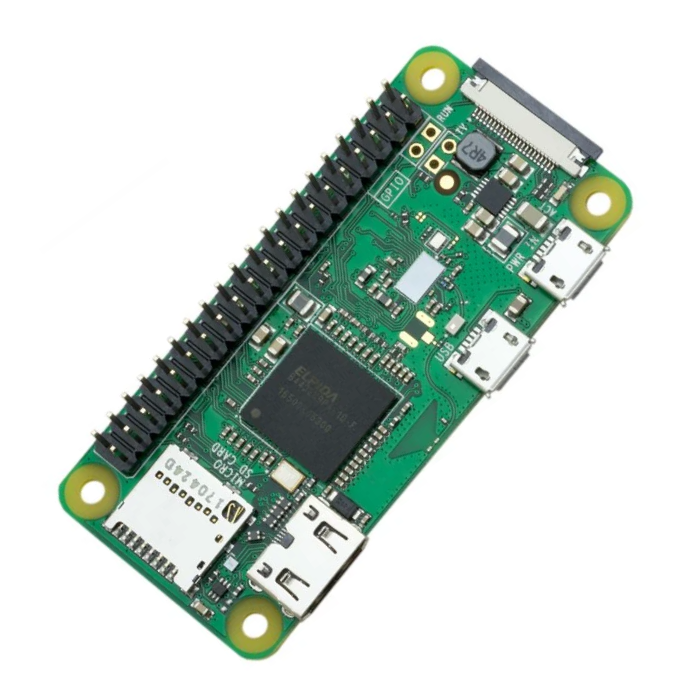
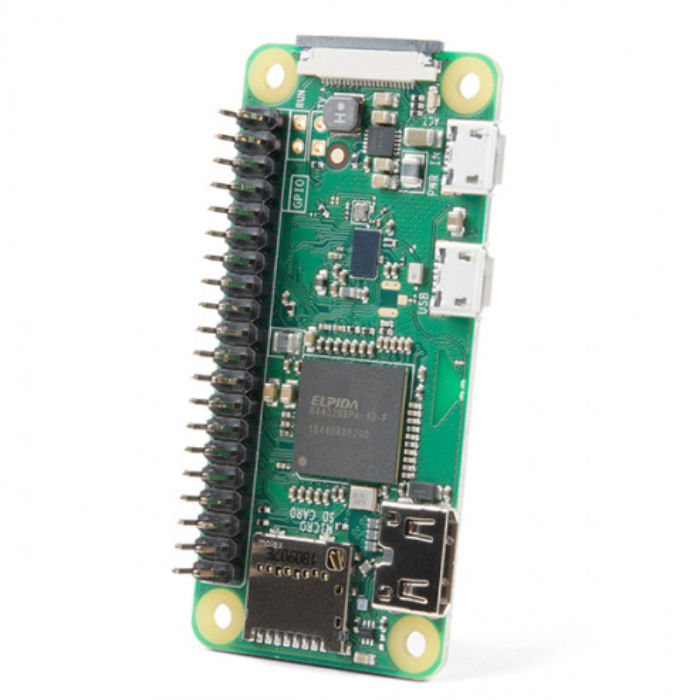
Dev kit working great with MQTT integration. On-point delivery, secure packing. Website offers tutorials. Technical support efficient for debug. Quality components enhance projects. Smooth from order to operation.
Excellent support guided module integration step-by-step. Quality components shine. Swift delivery, professional packing. Website easy navigation. Working reliably in my setup now. Positive experience from order to use.
Stable connection even through walls with TB-03F. Reliable delivery, robust packing. Website offers good FAQs. Customer support efficient for troubleshooting. Quality build for long use. Ideal wireless module choice.
Reliable delivery tracking updated real-time, module safe. Packing top-notch. Bluetooth module works flawlessly for data transfer. Website checkout secure. Technical support prompt on queries. Enhances my DIY gadgets superbly.
Efficient support sorted my signal interference fast. Quality components shine in tests. Prompt delivery, secure packing. Website offers FAQs galore. Wireless control reliable now. Great for DIY automation enthusiasts like me.