NEMA 17 Mounting L Bracket for Stepper Motor for 3d printer
Original Arduino UNO EK (एक) R4 Minima - Made in India
0.96 Inch OLED Display Module SPI/I2C 4pin Blue Color
F450 4-axis Quadcopter Drone Frame Kit with Integrated PCB (Black & White)
150W Dc-Dc Boost Adjustable Power Converter
Let us know!
We'll try to match the price for you
Couldn't load pickup availability
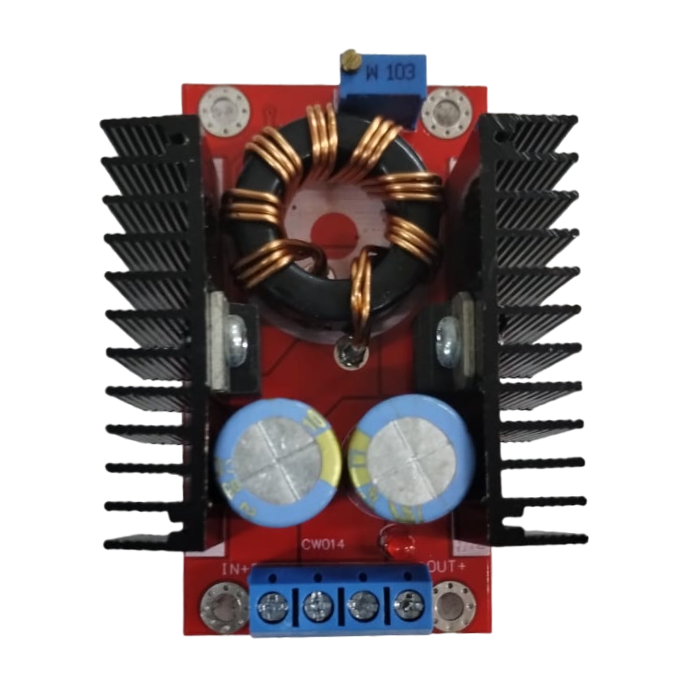
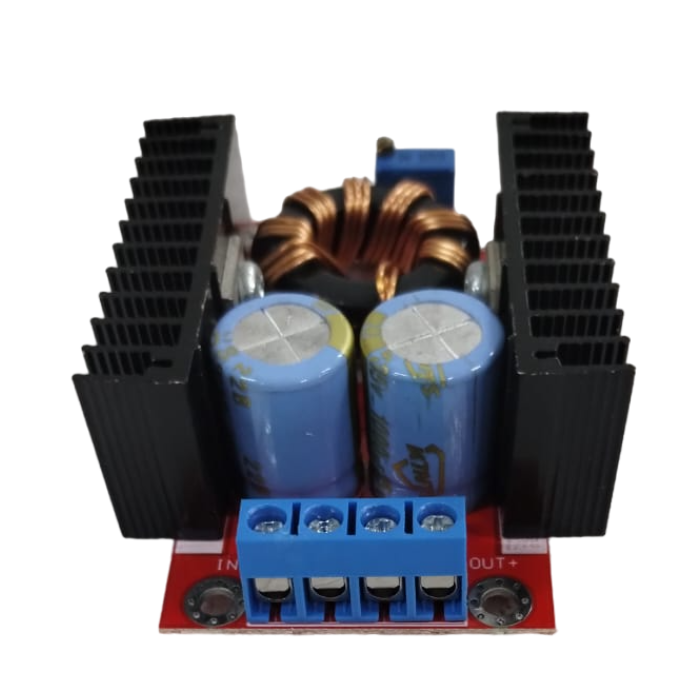
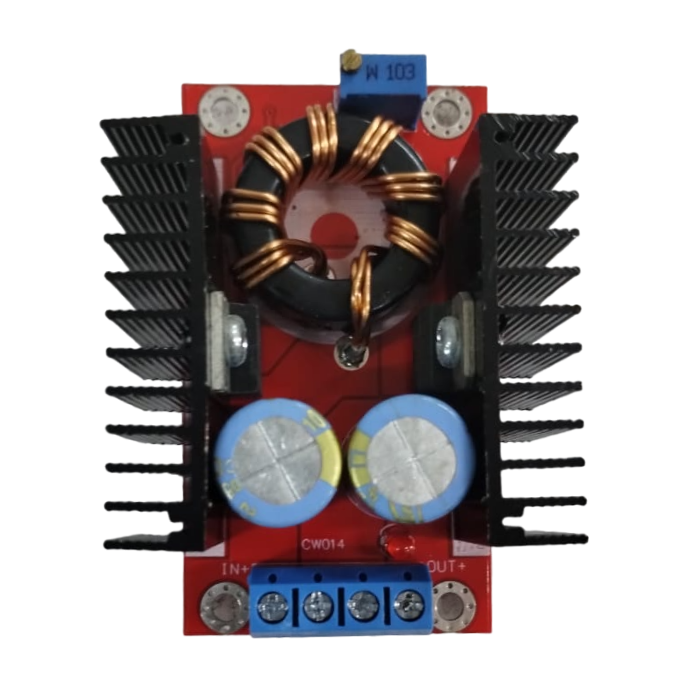
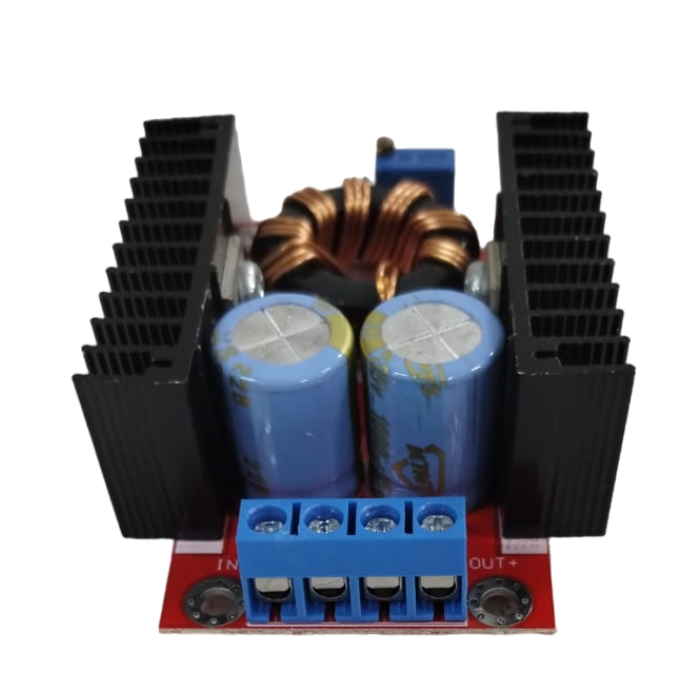
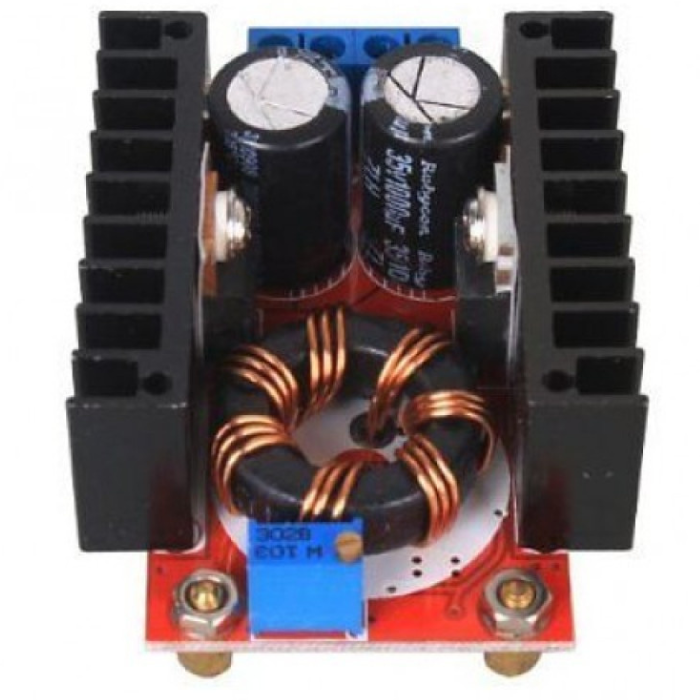
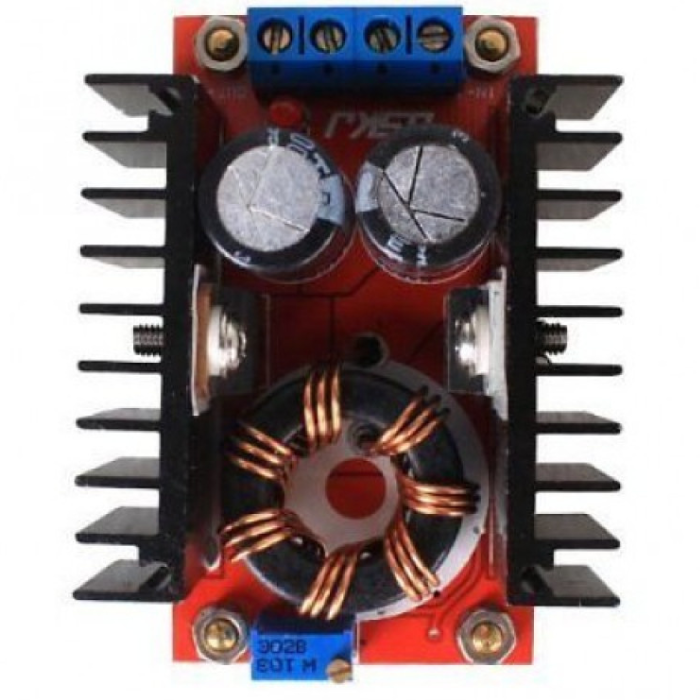







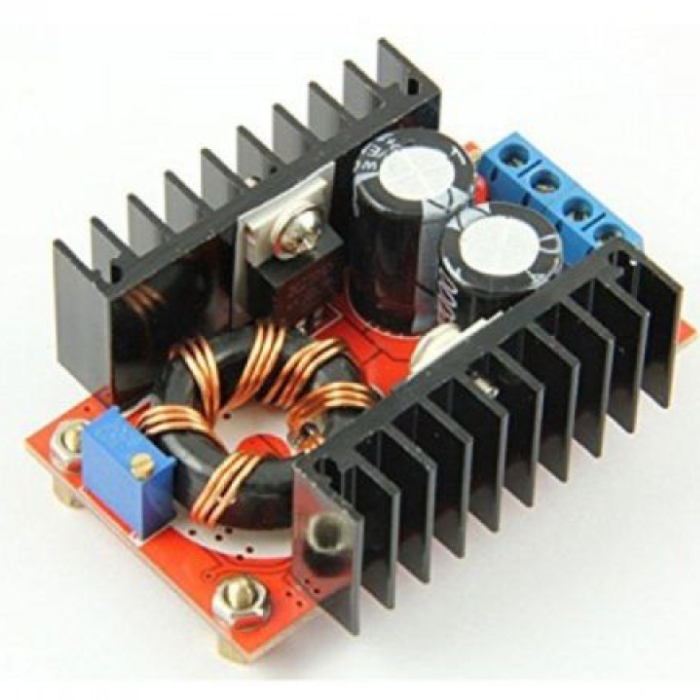

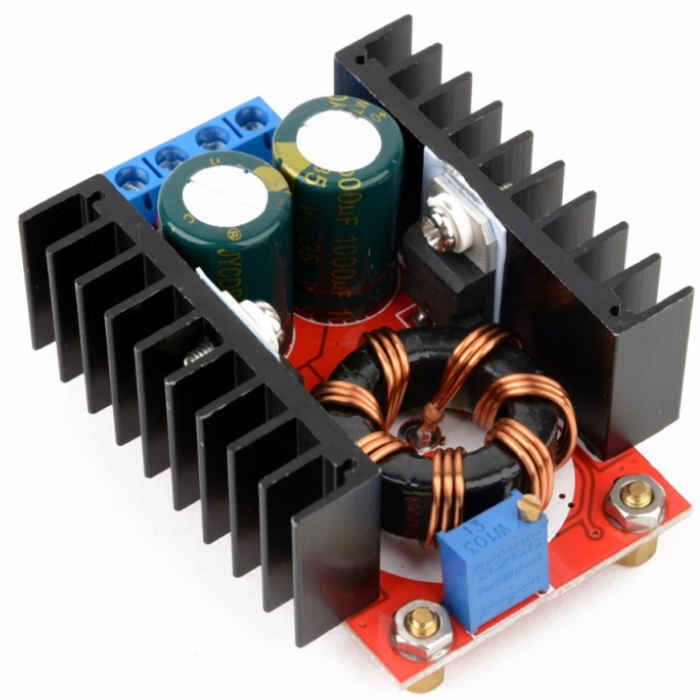

This DC-DC boost power supply/converter module is incredibly versatile, capable of stepping up any input voltage from 10V to 32V to an output voltage ranging from 12V to 35V. It can produce up to 150W of output power and a current of 6A. This Dc-Dc Boost Converter is heavy-duty, evidenced by the large toroidal inductor and dual heatsinks.
This module is especially useful for 12V automotive applications. It can boost standard 12V battery power to 19V for use as a laptop power supply or to 18V or 24V for other applications requiring higher voltages.
It is important to note that this module does not have reverse polarity protection. It is recommended to use a series diode, but for high loads, this may not be an option. Careful attention to the input polarity is crucial to avoid damaging the module.
| Power Converter Type | 150W Dc-Dc Boost Adjustable Power Converter |
| Input Voltage (V) | 10 to 32 |
| Input Current(A) | 10 |
| Output Voltage(V) | 12 to 35 |
| Max. Output Current (A) | 6 |
| Conversion Efficiency(%) | 94 |
| Dimensions | 3x2x1 cm |
A DC-DC boost converter is a switched-mode power supply that elevates the voltage of a DC input to a higher DC output voltage. This type of power converter employs at least two semiconductors, such as a diode and a transistor, to raise the voltage while lowering the current. It is often referred to as a step-up converter because it increases the source voltage. The output voltage of a boost converter surpasses the source voltage, while the output current is lower than the source current. Boost converters have numerous applications, such as driving a string of LEDs or charging a battery.
Boost converters have several advantages, including:
An inverter and a boost converter are two types of electrical devices that convert current, but they operate in opposite directions. A converter converts AC voltage to DC voltage or reduces a high voltage to a lower voltage, such as converting 110V to 12V in an RV. An inverter, on the other hand, transforms DC voltage to AC voltage or raises a low voltage to a higher voltage, such as converting 12V to 110V in an RV.
Meanwhile, a boost converter is a type of DC-DC converter that produces an output voltage that is greater than the input DC voltage.