
People Also Buy

NRF24L01 Ultra Low Power 2.4GHz RF Wireless Transceiver ( Pack of 25)
27 reviews
Regular price
Rs. 1,799
Regular price
Rs. 2,450
Sale price
Rs. 1799
Unit price
per
Incl. GST (No Hidden Charges)
Sold out

NRF51822
27 reviews
Regular price
Rs. 640
Regular price
Rs. 899
Sale price
Rs. 640
Unit price
per
Incl. GST (No Hidden Charges)
Sold out

RFM69 FSK Transceiver Module
27 reviews
Regular price
Rs. 297
Regular price
Rs. 349
Sale price
Rs. 297
Unit price
per
Incl. GST (No Hidden Charges)
Sale
Found a better price?
Let us know!
We'll try to match the price for you
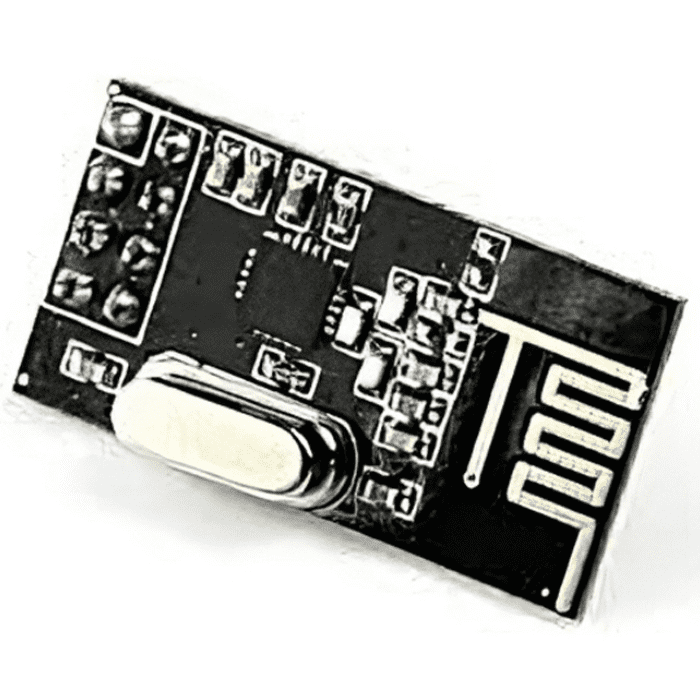
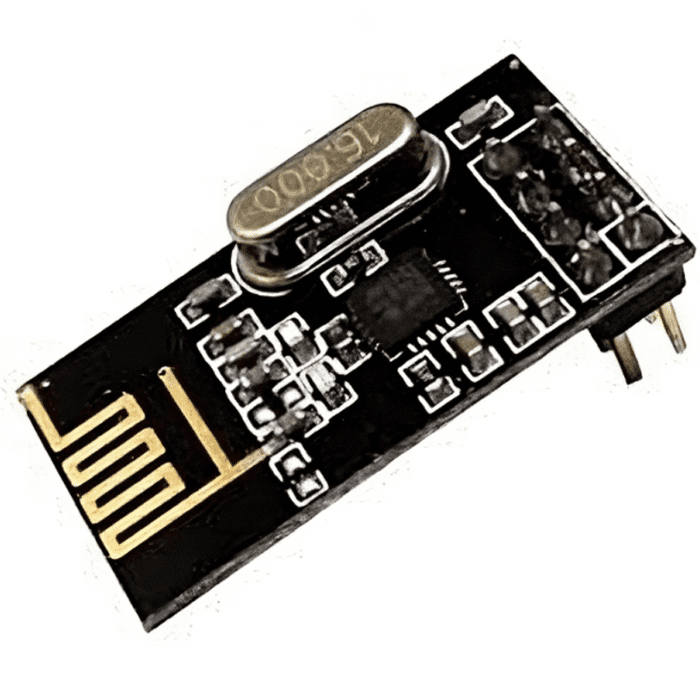
Package Includes:
- 1 x Nrf24L01 Ultra-Low Power 2.4Ghz RF Wireless Transceiver
Specifications
| High air data rate | 250kbps, 1 and 2Mbps |
| Host Interface | 4-pin hardware SPI,3 separate 32 bytes TX and RX FIFOs |
| Low Power Management | 1.9 to 3.6V supply range |
| Dimensions | 16.5mm*45.5mm |
| Weight | 5 grams |
1. What is the NRF24L01 transceiver?
- The nRF24L01 is a single-chip radio transceiver that operates in the 2.4-2.5 GHz ISM band all over the world. The transceiver consists of a fully integrated frequency synthesizer, a power amplifier, a crystal oscillator, a demodulator, a modulator, and an Enhanced ShockBurst protocol engine.
2. Is NRF24L01 a wireless module?
- NRF24L01 wireless module is a module with low power consumption which gives you a possibility to do wireless communication on 2.4GHz frequency. It has a communication speed of 2MBps, making it ideal for a variety of hobby, robotics, and industrial projects. It supports the SPI interface.
3. What is NRF24L01 used for?
- The NRF24L01 is an 8-pin wireless transceiver module with special pins that allow it to communicate with all boards and microcontrollers. The pin functions on this device are used to interface with an Arduino or an external microcontroller.
4. How do I know if NRF24L01 is working?
- One NRF24L01 should be connected to an Uno R3 and the other to a Mega2560. The nRF24L01 module on the UNO constantly sends data, while the one on Mega2560 receives it. Open the IDE and then Serial Monitor for the two boards respectively, and then compare the data sent and received to test whether it succeeds.














