What Is Pulse Sensor - Types and Its Applications
Summary
Do you want to discover the Power of Pulse Sensors? If the answer is yes! then this blog post is for you, we have covered everything from understanding what a pulse sensor is, to exploring its working principle, types, features and specifications, pin configuration, usage, and applications, this comprehensive guide will give you a complete overview of this versatile tool. Get the pulse of your projects and harness the full potential of pulse sensors. Don't miss out!
What is a Pulse Sensor?
Upon pumping blood through a blood vessel, the volume of the vessels expands, causing a change in the pulse wave.
A detector that monitors this volume change is a pulse rate sensor or pulse oximeter sensor and is used by doctors to check for signs of arrhythmia (unusually high blood pressure).

It's simple to check your pulse with just your fingers using either your wrist or the side of your neck, according to the Harvard Medical School Special Health Report on Diseases of the Heart.
Apply pressure at the wrist, just below the base of the thumb, with the index and middle fingers of one hand, below your jawbone, and lightly press the side of your neck.
Taking a count of heart in 15 seconds is multiplied by four is the number is your heart rate.
Microcontrollers such as Arduino and Raspberry Pi can be interfaced with a pulse sensor to receive alert messages when the heartbeat meets the threshold through sensing the heartbeat by a pulse sensor.
Pulse Sensor Working Principle
You may feel a pulse in some of the blood vessels close to the skin's surface when your heart pumps blood through your body, such as in your wrist, neck, or upper arm. How quickly your heart is beating can be easily determined by counting your pulse rate.
Students, artists, athletes, mobile and game developers can easily incorporate live heart rate data into their projects with the pulse sensor, which is designed to be an easy-to-use plug-and-play heart rate sensor. One requirement is that the sensor should clip onto a fingertip or earlobe or any part of the body that can measure the heartbeat accurately. With the help of jumper cables, it can easily connect to the microcontroller and get data or draw real-time graphs of your pulse.
A basic optical heart rate sensor is combined with this sensor via a circuit. This circuit is used to quickly obtain reliable pulse readings by amplifying and cancelling noise. It is excellent for mobile applications because it only consumes 4mA at 5V.

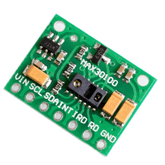
Now, let us look at what the sensor looks like from the front and back views shown above, as you can see a pretty heart shape on the side that contacts the skin. An LED is in the center of the sensor, and a little square below the LED is an ambient sensor used to eliminate the noise called Noise elimination circuitry. The back view of the sensor as the electronic components are mounted at the centre LED is reversely mounted. This is done because it does not meet the skin.
Types of the Pulse Sensor
To begin with, there are four main methods of measuring heart rate: electrocardiogram, photoelectric pulse wave, and blood pressure measurement.
Pulse sensors are implemented by a photoelectric method.

Transmission Type
During heartbeats, transmission types detect the change in blood flow as a change in the amount of light transmitted through the body by emitting red or infrared light. A fingertip or earlobe is a good area to place the sensor because light can easily penetrate there.
Reflection Type
This type of heart rate sensor produces infrared, red, or green light that is directed at the human body and then detects the light that is reflected off a phototransistor or photodiode. Oxygenated hemoglobin, which is found in the arteries of humans, can absorb light. We can compute the pulse signal by identifying the blood flow rate that fluctuates at the precise moment that the heart begins to pump. To avoid an unstable operation, IR rays should be minimized in sunlight while measuring pulse wave signals using red or IR light. This is the case, so indoors or semi-indoors are used. A green-coloured source has a high rate of absorption within the hemoglobin and is used for pulse wave measurement.
In other words, A photodiode or phototransistor is used to quantify the amount of light reflected by the body via reflection-type pulse sensors (Optical Sensors for Heart Rate Monitor), which produce infrared, red, or green light (550nm) in the direction of the body.
We can measure the pulse wave signal by detecting the blood flow rate (change in blood vessel volume) that changes over time because of cardiac contractions because oxygenated hemoglobin, which is present in the blood of the arteries, has the property of absorbing incident light.
Additionally, unlike with transmission-type pulse sensors, the range of eligible regions is not constrained because reflected light is detected.
Features and specifications
Features:
- This sensor measures the heart rate and biometric pulse rate.
- This heart rate sensor is a plug-and-play model.
- This sensor operates at a voltage of +5V/+3.3V.
- Integral amplification circuit for noise cancellation,
- Low power consumption
Specifications
|
Specifications |
Parameters |
|
maximum current |
100mA |
|
Heartbeat deduction output |
LED |
|
VCC |
+5v DC (high-quality regulation) |
|
Light source |
660nm super Red LED |
|
Output data level |
5V TTL |
Pin Configuration

There are three pins in the sensor module GND, VCC and analog pins.
How to use Pulse Sensor
If you have ever checked your heart rate by shining a flashlight on your fingertips, the theory of optical heart rate sensors should be solid.
A pulse sensor, or any optical heart rate sensor, works by shining a green light (~550 nm) on your finger and measuring the amount of reflected light with a photo sensor.
Oxygen-rich hemoglobin in arterial blood has the property of absorbing green light. The redder the blood (higher the hemoglobin level), the greener light it absorbs.
As blood is pumped out of the finger with each heartbeat, the amount of reflected light changes, producing a varying waveform at the output of the light sensor.
You can read your heart rate immediately by exposing it to light and continuing to read the photosensor.
Since this signal from a photo sensor is typically small and noisy, the signal is passed through an R/C filter network and amplified with an op-amp to produce a much louder, cleaner, and easier-to-see signal.
To get analog data from the sensor, pulse sensors can be interfaced with a microcontroller such as Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or any other controller.
Circuit Diagram

|
Arduino UNO |
Pulse Sensor |
|
5V |
VCC |
|
GND |
GND |
|
A0 |
A0(Analog Pin) |
Code
Download the Arduino Sketch coding software on the computer. You write the code here, which will be compiled and uploaded to the Arduino board.
Before uploading the code, you must add the “PulseSensorPlayground” library to IDE. For getting basic code go to File >> Examples >>Pulse sensor or copy and paste the below simple code to your IDE.
#define USE_ARDUINO_INTERRUPTS true
#include <PulseSensorPlayground.h>
const int PulseWire = 0;
const int LED13 = 13;
int Threshold = 550;
PulseSensorPlayground pulseSensor;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pulseSensor.analogInput(PulseWire);
pulseSensor.blinkOnPulse(LED13);
pulseSensor.setThreshold(Threshold);
if (pulseSensor.begin()) {
Serial.println("We created a pulseSensor Object !");
}
}
void loop() {
int myBPM = pulseSensor.getBeatsPerMinute();
if (pulseSensor.sawStartOfBeat()) {
Serial.println(" A HeartBeat Happened ! ");
Serial.print("BPM: ");
Serial.println(myBPM);
}
delay(20);
}
Applications of Pulse Sensor
- Sleep Tracking: Usually heartbeat is lower at the time of sleep.
- Monitoring of anxiety: When anxiety happens heartbeat increases gradually that is measured by the pulse sensor
- Alarm system: When the heartbeat reaches to threshold alarm will activate automatically.
- Remote patient monitoring: If the patients are in a remote area, then this sensor can monitor the patient's heartbeat and relay it to a remote location using IoT.
- Health bands
- Advanced gaming consoles
Conclusion
In this blog post, we have learned a pulse sensor is a revolutionary device that measures and tracks the rhythmic beat of one's heart, detecting pulse signals with unparalleled accuracy. Its working principle is based on the detection of blood flow, rendering it an indispensable tool for a wide spectrum of applications, from healthcare to sports and beyond. With its various types, striking features, intricate pin configurations, and versatility, the pulse sensor is a must-have for anyone seeking to monitor their pulse signals with unrivalled precision. So ignite your pulse, seize the moment, and experience the thrill of pulse monitoring with the pulse sensor, today!
If you appreciate our work don't forget to share this post and leave your opinion in the comment box.
Please do check out other blog posts about Popular electronics
Make sure you check out our wide range of products and collections (we offer some exciting deals!)
Excerpt
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the pulse sensor?
A pulse sensor is an enigmatic device, utilized to keep a vigilant watch on one's heartbeat. It leverages the fluctuation in the volume of blood coursing through the arterial veins to ascertain the rhythmic beats of a person's heart. Often employed in medical and fitness domains, this cunning device can be fastened onto various parts of the anatomy such as the wrist, earlobe, finger or neck. Its modus operandi is to detect alterations in blood flow, transforming this information into an electrical signal that can be interpreted by a monitor or any other technologically advanced device.
2. Where is a pulse sensor used?
A pulse sensor measures the flow of blood through the arteries, by detecting changes in the pulse. It is placed on the delicate wrist, the sensitive finger or the modest earlobe, and like a messenger from the underworld, it sends forth cryptic signals to a monitor, where it deciphers the beating heart into a numerical value, expressed in Beats Per Minute (BPM). This mysterious technology is widely used in the medical arena, as well as in the fitness world, and in the realm of wearable tech, to monitor the ever-beating heart.
3. Is pulse sensor analog or digital?
The Pulse Sensor is an enigmatic analog device that gauges the fluctuation in luminosity resulting from the ebb and flow of blood within a digit and emits an enigmatic analog signal. This signal is then subjected to a mystical analog-to-digital conversion process to yield a cryptic digital interpretation of the pulse rate, providing an insight into the mystic rhythm of the user's heart.
4. What is a pulse sensor and how does it measure heart rate?
A pulse sensor is a device that detects blood flow through the skin to measure heart rate. It typically uses light transmission, where an LED shines through the skin, and the amount of light absorbed by the blood is measured. This data is processed to provide an accurate reading of beats per minute, making it suitable for health monitoring and fitness applications.
5. What are the different types of pulse sensors (optical, capacitive)?
There are two main types of pulse sensors: optical and capacitive. Optical pulse sensors use light to detect blood flow, while capacitive sensors measure the electrical capacitance changes due to blood movement. Optical sensors are more common for heart rate monitoring, offering better accuracy and ease of use.
6. How do you interface a pulse sensor with Arduino?
To interface a pulse sensor with Arduino, connect the sensor's output pin to an analog pin on the Arduino. Use power and ground connections as specified in the sensor's documentation. Then, utilize Arduino libraries like "PulseSensor" to read and process data, allowing real-time heart rate monitoring and analysis in your projects.
7. What is the difference between a pulse sensor and a pulse oximeter?
A pulse sensor measures heart rate by detecting changes in blood flow, while a pulse oximeter measures blood oxygen levels. Pulse oximeters utilize visible and infrared light to assess the oxygen saturation in the blood, making them ideal for respiratory assessments, whereas pulse sensors focus solely on heart rate.
8. What applications use pulse sensors in DIY electronics?
Pulse sensors are commonly used in DIY electronics for health monitoring, fitness trackers, and medical devices. Applications include wearable technology, heart rate monitors, and even data logging in Arduino projects for biosignal analysis, promoting awareness of personal health metrics.
9. How accurate are pulse sensors for heart-rate monitoring?
Pulse sensors can provide accurate heart rate readings, usually within a margin of 5 BPM. However, accuracy may vary based on factors like skin tone, movement, and ambient light. For best results, ensure proper sensor placement and keep the subject still during measurement.
10. What are the limitations of low-cost pulse sensors?
Low-cost pulse sensors often face limitations in accuracy, sensitivity, and range. They may struggle with motion artifacts or poor performance under varying skin conditions. Environmental factors like ambient light interference can also affect readings, making them less reliable than higher-end models.
11. Can a pulse sensor detect arrhythmia or irregular beats?
Basic pulse sensors can indicate heart rate irregularities but lack the specificity to diagnose arrhythmia. For accurate detection of arrhythmias or irregular beats, advanced ECG or more specialized devices are required, as pulse sensors primarily focus on overall heart rate output.
12. What power and wiring considerations exist for pulse sensors?
When using pulse sensors, ensure they are powered correctly, typically requiring 3.3V or 5V from your microcontroller. Proper wiring is essential, connecting the signal, power, and ground pins correctly to avoid damage. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for optimal performance and safety.
13. How do you filter and process the pulse signal for stable reading?
To filter and process the pulse signal, implement software algorithms like moving averages or low-pass filters. These techniques help reduce noise and enhance the stability of heart rate readings. Use libraries compatible with your microcontroller for easier integration and real-time data processing.
1. What is the pulse sensor?
A pulse sensor is an enigmatic device, utilized to keep a vigilant watch on one's heartbeat. It leverages the fluctuation in the volume of blood coursing through the arterial veins to ascertain the rhythmic beats of a person's heart. Often employed in medical and fitness domains, this cunning device can be fastened onto various parts of the anatomy such as the wrist, earlobe, finger or neck. Its modus operandi is to detect alterations in blood flow, transforming this information into an electrical signal that can be interpreted by a monitor or any other technologically advanced device.
2. Where is a pulse sensor used?
A pulse sensor measures the flow of blood through the arteries, by detecting changes in the pulse. It is placed on the delicate wrist, the sensitive finger or the modest earlobe, and like a messenger from the underworld, it sends forth cryptic signals to a monitor, where it deciphers the beating heart into a numerical value, expressed in Beats Per Minute (BPM). This mysterious technology is widely used in the medical arena, as well as in the fitness world, and in the realm of wearable tech, to monitor the ever-beating heart.
3. Is pulse sensor analog or digital?
The Pulse Sensor is an enigmatic analog device that gauges the fluctuation in luminosity resulting from the ebb and flow of blood within a digit and emits an enigmatic analog signal. This signal is then subjected to a mystical analog-to-digital conversion process to yield a cryptic digital interpretation of the pulse rate, providing an insight into the mystic rhythm of the user's heart.
4. What is a pulse sensor and how does it measure heart rate?
A pulse sensor is a device that detects blood flow through the skin to measure heart rate. It typically uses light transmission, where an LED shines through the skin, and the amount of light absorbed by the blood is measured. This data is processed to provide an accurate reading of beats per minute, making it suitable for health monitoring and fitness applications.
5. What are the different types of pulse sensors (optical, capacitive)?
There are two main types of pulse sensors: optical and capacitive. Optical pulse sensors use light to detect blood flow, while capacitive sensors measure the electrical capacitance changes due to blood movement. Optical sensors are more common for heart rate monitoring, offering better accuracy and ease of use.
6. How do you interface a pulse sensor with Arduino?
To interface a pulse sensor with Arduino, connect the sensor's output pin to an analog pin on the Arduino. Use power and ground connections as specified in the sensor's documentation. Then, utilize Arduino libraries like "PulseSensor" to read and process data, allowing real-time heart rate monitoring and analysis in your projects.
7. What is the difference between a pulse sensor and a pulse oximeter?
A pulse sensor measures heart rate by detecting changes in blood flow, while a pulse oximeter measures blood oxygen levels. Pulse oximeters utilize visible and infrared light to assess the oxygen saturation in the blood, making them ideal for respiratory assessments, whereas pulse sensors focus solely on heart rate.
8. What applications use pulse sensors in DIY electronics?
Pulse sensors are commonly used in DIY electronics for health monitoring, fitness trackers, and medical devices. Applications include wearable technology, heart rate monitors, and even data logging in Arduino projects for biosignal analysis, promoting awareness of personal health metrics.
9. How accurate are pulse sensors for heart-rate monitoring?
Pulse sensors can provide accurate heart rate readings, usually within a margin of 5 BPM. However, accuracy may vary based on factors like skin tone, movement, and ambient light. For best results, ensure proper sensor placement and keep the subject still during measurement.
10. What are the limitations of low-cost pulse sensors?
Low-cost pulse sensors often face limitations in accuracy, sensitivity, and range. They may struggle with motion artifacts or poor performance under varying skin conditions. Environmental factors like ambient light interference can also affect readings, making them less reliable than higher-end models.
11. Can a pulse sensor detect arrhythmia or irregular beats?
Basic pulse sensors can indicate heart rate irregularities but lack the specificity to diagnose arrhythmia. For accurate detection of arrhythmias or irregular beats, advanced ECG or more specialized devices are required, as pulse sensors primarily focus on overall heart rate output.
12. What power and wiring considerations exist for pulse sensors?
When using pulse sensors, ensure they are powered correctly, typically requiring 3.3V or 5V from your microcontroller. Proper wiring is essential, connecting the signal, power, and ground pins correctly to avoid damage. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for optimal performance and safety.
13. How do you filter and process the pulse signal for stable reading?
To filter and process the pulse signal, implement software algorithms like moving averages or low-pass filters. These techniques help reduce noise and enhance the stability of heart rate readings. Use libraries compatible with your microcontroller for easier integration and real-time data processing.